41 dosage calculations from medication labels
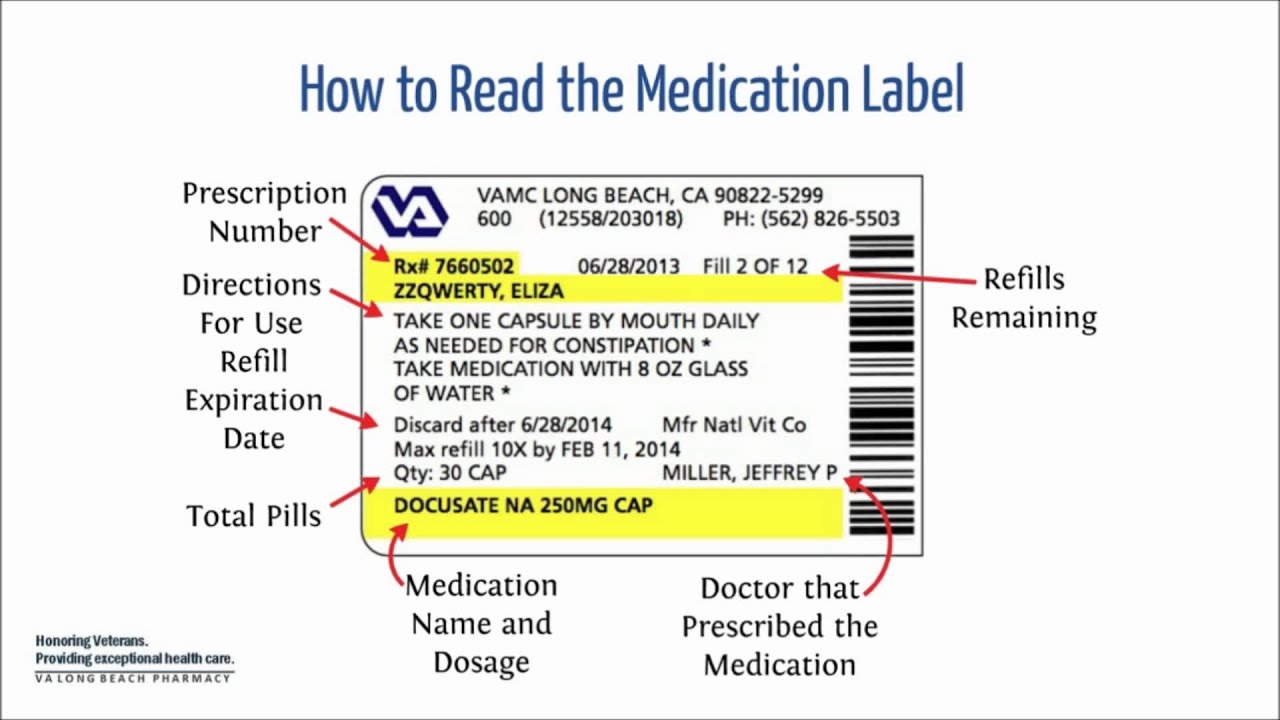
Provide Dose Calculation Aids on Drug Labels - IHI A calculation aid placed directly on the label means staff members administering medications need not make any calculations. A calculation aid on an infusion bag might list several different doses and the flow rates to set to achieve each one, based on the size of the bag and the concentration of the solution. Lecture 3: Reading Medication Labels and Basic Dosage Calculations Every tenth of a mLis marked on the syringe, and every half mL is labeled; this means that any dosage we plan to measure using a 3 mL syringe should be rounded to the nearest tenth. Dosages between 1-3 mLshould always be measured in a 3 mL syringe.
Dose Calculation Dimensional Analysis Factor-Label Method Introduction. Three primary methods for calculation of medication dosages exist, and these include dimensional analysis, ratio proportion, and formula or desired-over-have method. This article explores dimensional analysis in more detail. Dimensional analysis, as the name represents, explores dimensions or units of measurements called factors.

Dosage calculations from medication labels
Drug Calculations Practice NCLEX Questions (100+ Items) - Nurseslabs Methods for Drug Dosage Calculations Standard Method The commonly used formula for calculating drug dosages. Where in: D = Desired dose or dose ordered by the primary care provider. H = dose on hand or dose on the label of bottle, vial, ampule. V = vehicle or the form in which the drug comes (i.e., tablet or liquid). STANDARD FORMULA MedCal CH13: Reading Medication Labels Flashcards | Quizlet Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like a. Hemabate b. carboprost tromethamine c. 250 mcg per mL d. 1 mL e. Intramuscular (IM) use only f. Refrigerate at 2° C to 8° C (36° F to 46° F), Dosage strength of erythromycin: 200 mg per 5 mL reconstituted Dosage strength of sulfisoxazole: 600 mg per 5 mL reconstituted Total volume: 100 mL when mixed Form: oral suspensio, 4 ... Dosage Calculations 9th Edition - edocs.utsa.edu infusions is included. Drug labels are current, and problems use JCAHO-approved abbreviations. A handy quick-reference plastic pull-out card shows conversions and formulas. Nursing Dosage Calculation Workbook: 24 Categories of Problems from Basic to Advanced! Chase Hassen 2019-03-10 Are you a nursing student, or nurse, who has the basics of ...
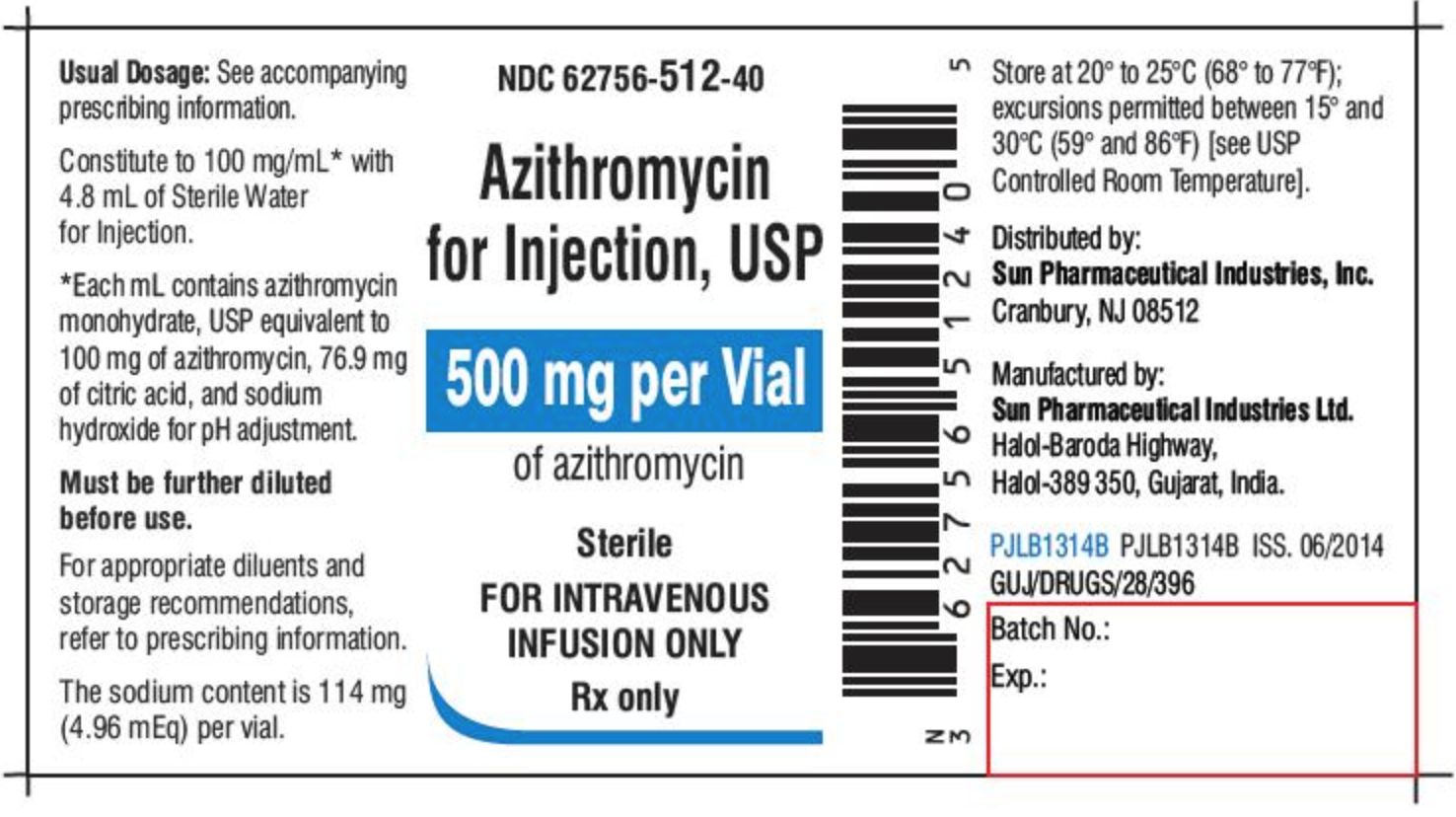
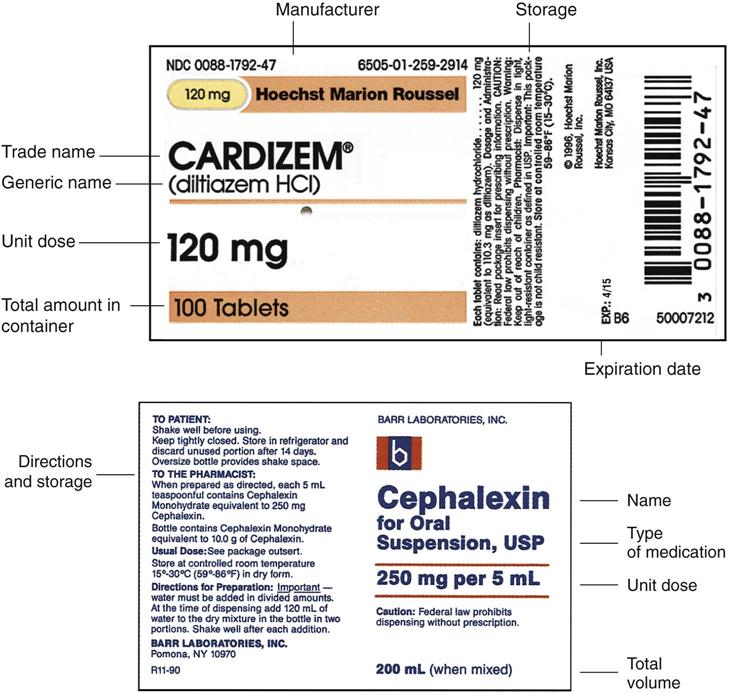
Dosage calculations from medication labels. PDF Formulas for Calculating Medication Dosage - Indian Hills Community College the medication label, and Q (quantity) is the volume in which the dosage strength is available (e.g. tablets, capsules, milliliters). For example: we have an order for Ceclor 0.5 g PO b.i.d. We have available 250 mg capsules. The first thing to do is get like units of measurement. Since we have 250 mg capsules, let's change our ordered dose ... Dosage Calculation Reading Drug Labels - StuDocu Dosage Calculation: Reading Drug Labels Chapter 11 Tarleton State University NURS 3310 Dr. Mary B. Winton Reading Drug Labels a. Brand/trade name b. Generic name c. Formulation d. Dosage strength e. Route f. Need prescription or Over -the-counter Reading Drug Labels and Reconstitution a. Generic name b. Brand/trade name c. Formulation d. Route e. Chapter 6 Oral Medication Labels and Dosage Calculation - SlideToDoc.com Chapter 17 dosage calculation and medication administration; Dosage on hand formula; Medication calculation formula; Reconstitution of medication; Medication administration test answers Lecture 3: Reading Medication Labels and Basic Dosage Calculations Dosage units: mg This one is a little tricky because the label does not actually state what the units are! However, because mg are the most commonly used units for drug dosages, we are supposed to assume that the 750 on the label means 750 mg.
Medical Dosage Calculations Actual drug labels are real-life examples of what is used in health care settings. The most. medical-dosage-calculations 12/23 Downloaded from ... Calculation of Medication Dosages Janice F. Boundy 2008 This text equips nurses with the decision making skills to ensure that medication dosages are calculated Medications and Calculations | Nurse Key This information is then used in correctly calculating the drug dose. Six calculation methods are explained. Four are general methods: (1) basic formula, (2) ratio and proportion, (3) fractional equation, and (4) dimensional analysis. The nurse should select one of these general methods for the calculation of drug dosages. Dosage Calculation Resources - Calhoun Community College 5:00 pm to 7:00 pm. Room 105, Health Sciences Building. Decatur Campus. Option B: In the Testing Center (computer exam) Sept 19-22, 2022 at your convenience for $13.50. Locations at Decatur and Huntsville Campuses. Out-of-State applicants may test remote online for a proctoring fee. Contact Misty.greene@calhoun.edu for more information. Dosage Calculations: NCLEX-RN - Registered nursing Medication label: 1 tablet = 250 mg How many tablets should be administered daily? In this problem you have to determine how many tablets the patient will take if the doctor order is 125 mg a day and the tablets are manufactured in tablets and each tablet has 250 mg. This problem can be set up and calculated as shown below.
PDF Medication Calculation Examination Study Guide - Los Angeles County ... Label shows 75 - 150 mg/kg per day. Is the physician's order within normal range? Solution: 6 x 75 = 450 mg (minimum dosage per day); 150 X6 = 900 (maximum dosage per day) 24 ÷ 4 = 6 dosages : 300 x 6 = 1800. Answer: Dosage is not within range. IV Calculations • [amount of fluid to be infused] x [drop factor] ÷ minutes to infuse = gtts/min Dosage Calculator - How to Calculate Dosage? Determine the dosage of the medication. Let's say the appropriate dosage of the active substance is 2 mg/kg of body weight. Weigh yourself. Let's assume you weigh 80 kg. Multiply these two values to get the dose of medication in mg: 2 * 80 = 160 mg. You need to take 160 mg of active substance. What if your medication is liquid? How to Read a Medication Label Nursing Skill - Medication ... - YouTube Reading a medication label (drug label): medication administration (dosage and calculations) NCLEX pharmacology / new nurse review.Reading medication labels ... PDF Dosage Calculations Syllabus(1)new - Odessa College Chapter 6: Oral medication labels and dosage calculations (CO #1-5) The learner will: 1. Identify scored tablets, unscored tablets, and capsules. 2. Read drug labels to identify trade and generic names. 3. Locate dosage strengths and calculate average dosages. 4. Measure oral solutions using a medicine cup. Chapter 7: Safe medication administration
Drug Calculations Involving Reading Drug Labels, Part 1 - YouTube Practice performing drug dosage problems that require the use and understanding of drug labels to solve. Problem 1.) Determine the milliliters of Augmentin required. Problem 2.) Determine...
Drug Dosage Calculations | How-to-guide - KnowledgeDose What is the correct dosage on the label? Take 800 units (0.4ml) once daily Take 800 units (0.8ml) once daily Take 800 units (0.6ml) once daily Take 800 units (1ml) once daily 78 Likes About KnowledgeDose
PDF Drug dosage calculation handout for BSN completion Dosage by weight (with label) 2 Continuous IV med (flow rate or medication delivered) 2 Direct IV (IV push) (with label if possible) 2 Total 20 Recommended text: Olsen, J., Giangrasso, A. & Shrimpton, D. (2015). Medical dosage calculations: A dimensional analysis approach. Boston, MA: Pearson
Dosage Calculations 9th Edition - edocs.utsa.edu infusions is included. Drug labels are current, and problems use JCAHO-approved abbreviations. A handy quick-reference plastic pull-out card shows conversions and formulas. Nursing Dosage Calculation Workbook: 24 Categories of Problems from Basic to Advanced! Chase Hassen 2019-03-10 Are you a nursing student, or nurse, who has the basics of ...
MedCal CH13: Reading Medication Labels Flashcards | Quizlet Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like a. Hemabate b. carboprost tromethamine c. 250 mcg per mL d. 1 mL e. Intramuscular (IM) use only f. Refrigerate at 2° C to 8° C (36° F to 46° F), Dosage strength of erythromycin: 200 mg per 5 mL reconstituted Dosage strength of sulfisoxazole: 600 mg per 5 mL reconstituted Total volume: 100 mL when mixed Form: oral suspensio, 4 ...
Drug Calculations Practice NCLEX Questions (100+ Items) - Nurseslabs Methods for Drug Dosage Calculations Standard Method The commonly used formula for calculating drug dosages. Where in: D = Desired dose or dose ordered by the primary care provider. H = dose on hand or dose on the label of bottle, vial, ampule. V = vehicle or the form in which the drug comes (i.e., tablet or liquid). STANDARD FORMULA







.png)













Post a Comment for "41 dosage calculations from medication labels"